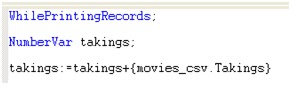
Crystal report works great when the export feature is used
to export reports to PDF and word, but the one real drawback is the ‘Export to
Excel’ feature. No matter how well you in designing the crystal report, the
export to excel output is always skewed. It is the way Crystal Report runtime
engine maps the objects and places them in excel cells based on the (x,y)
position of the original Crystal Objects in the .RPT file.
I did not like how the default export feature was working on
crystal reports and also wanted new features like:
- More uniform export to excel feature with less dummy rows and columns and more visually appealing output.
- Restrict the number of export features to only Excel, PDF and Microsoft word and remove all the unnecessary list of export options that the system provides.
- Control over Export file fonts, regardless of what font the Crystal report was developed on.
- A friendly option in the ‘Export Successful ‘message box for users to click on a link which opens the export file for them without going to the folder where the report was exported.
- Fixed width of rows for uniformity.
So let’s begin the process on steps:
Step 1: Assumptions
- You are using Visual Studio 2005 or higher.
- Crystal Report viewer is hosted in a windows form ‘ReportViewer.cs’
- The example is for the report being exported to excel but it can be used for export to other formats
Step 2: Load data to the report via XML or Memory Stream
private ReportDocument myReport = null;
private void ReportViewer_Load(object sender, EventArgs e)
{
myReport = new ReportDocument();
myData = new DataSet();
try
{
switch (_inputType)
{
case DataInputType.ByteArray:
myData.ReadXml(new System.IO.MemoryStream(_reportData));
break;
case DataInputType.MemoryStream:
stream.Seek(0, SeekOrigin.Begin);
myData.ReadXml(_stream);
break;
}
//Load RPT file
myReport.Load(reportPath + _RPTName);
myReport.SetDataSource(myData);
crystalReportViewer1.ShowFirstPage();
crystalReportViewer1.ShowGroupTreeButton = true;
crystalReportViewer1.ReportSource = myReport;
}
catch (Exception ex)
{
ErrorHandler.PublishError(false, "Error displaying report.", ex, true, true);
}
}